Pulse Oximetry
A revolutionary technology that allows blood oxygen saturation to be measured painlessly, continuously and in real time.
A technology that measures the oxygen in arterial blood (Arterial blood oxygen saturation: SpO_{2}) by a sensor attached the patient's finger or ear.
As a result of the COVID-19 pandemic, many people have become familiar with the term "Pulse Oximeter".
The principle of the pulse oximeter was discovered by the Nihon Kohden engineer Takuo Aoyagi in 1974.
Before that SpO_{2} measurement required sampling of arterial blood, which was painful for the patient and required time before the results were available.
Thanks to the pulse oximeter, medical professionals have become able to measure this important parameter continuously, painlessly and in real time, with the result that surgery under general anesthetic has become dramatically safer.
This revolutionary measurement technology has become indispensible in clinical practice around the world for safety management and monitoring the patient condition.
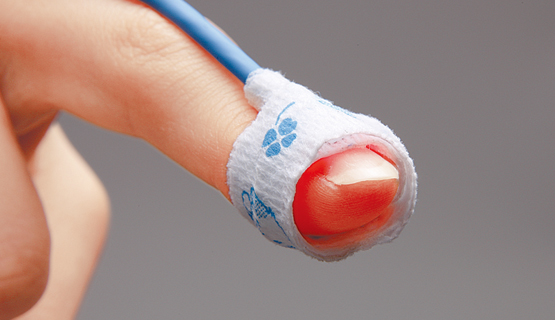
A sensor applied to the fingertip
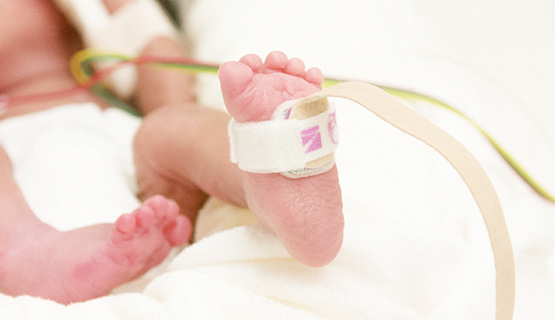
Sensor developed for use with small infants. It can also be attached to the foot.
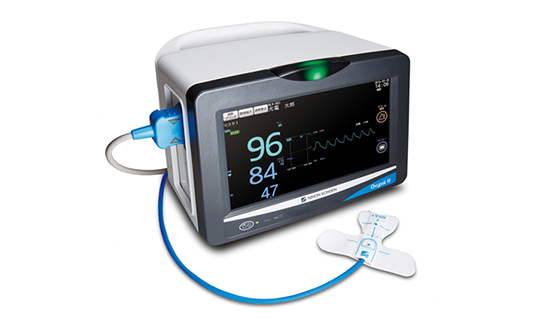
Pulse oximeters are widely used in the OR and other clinical settings
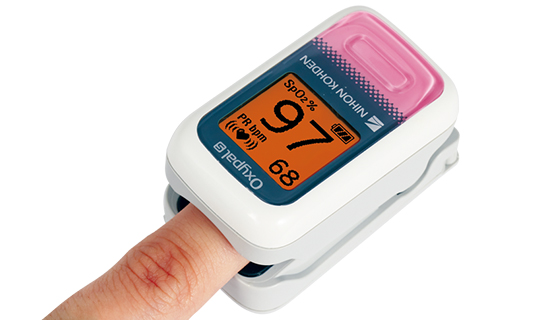
A pulse oximeter with the measurement and display components in one piece

